Wireless connectivity: Protocols adapted to each type of application
Connectivity protocols have diversified with the proliferation of connected objects to offer, for each application, the best possible compromise between range, throughput/measurement frequency, quality of service and reliability, consumption, lifespan and cost.
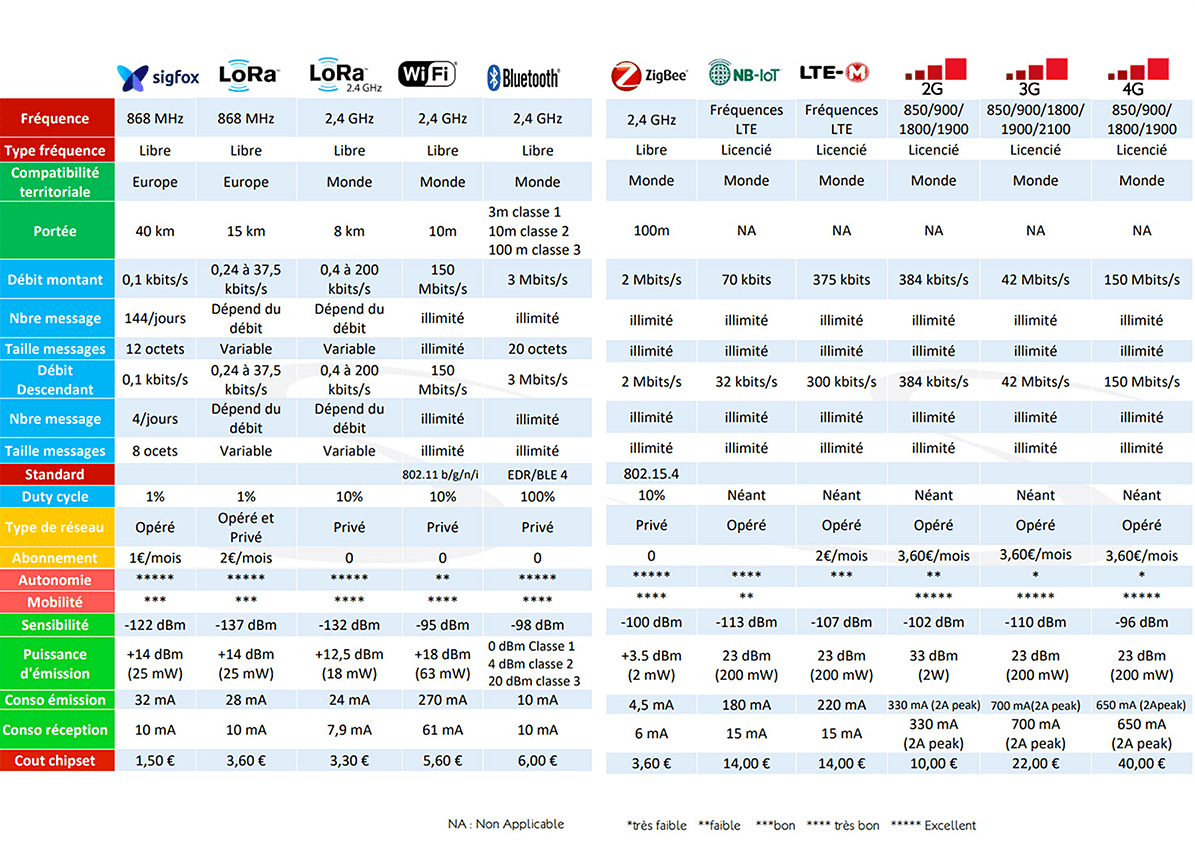
Here are some parameters on which they can be compared:
- Range: some protocols have a limited range, while others can cover greater distances.
- Power consumption: some protocols are more energy efficient than others, which is important for battery-powered connected objects.
- Bandwidth: some protocols have higher bandwidth than others, which is important for connected objects that require fast data transmission.
- Security: some protocols offer better security than others, which is important for connected objects that store sensitive data.
- Compatibility: certain protocols are more compatible with certain types of connected objects than others.
Depending on these parameters, connectivity protocols can be classified into different categories:
- short-range protocols (Bluetooth, Zigbee),
- long-range protocols (LoRaWAN, NB-IoT),
- low consumption protocols (Z-Wave, Thread), etc.
Example of a comparative table on a non-exhaustive list of protocols:
Source : symes.fr

